Software Licensing - Comprehensive Guide to Types and Models
Defining Software Licensing
Software licensing encompasses a contractual agreement that outlines the permissible usage of various software programs, ensuring legal compliance. These licenses establish guidelines for fair usage and intellectual property rights. Generally, software licenses fall into two categories: open-source and proprietary.
How Software Licenses Operate
At its core, a software license serves as a mechanism to define the rights and responsibilities of both the software vendor and the user. These rights and responsibilities are presented in the form of an end-user license agreement, which outlines the terms and conditions of usage. It may also specify the level of access granted to the software’s source code. It is essential for users to agree to these terms before legally obtaining the software.
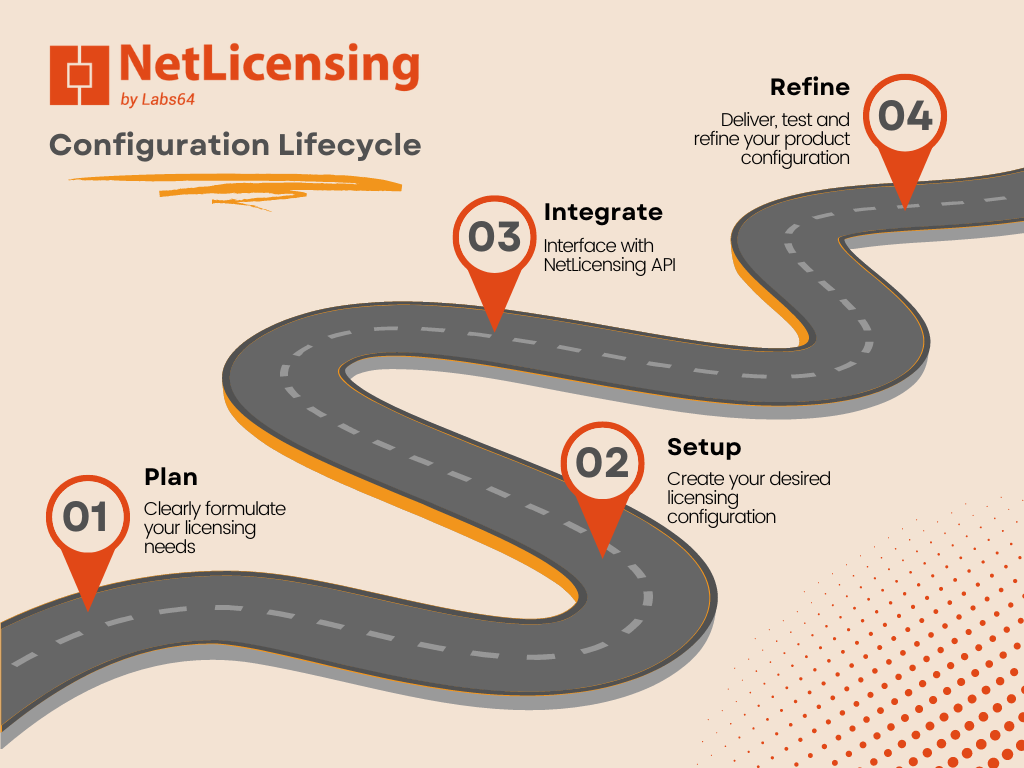
The Types of Software License Agreements
- PUBLIC DOMAIN: Software under this license is not protected by copyright. Users have the freedom to use and modify the software as they wish.
- LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE (LGPL): This license permits the linking of open-sourced libraries with the user’s own software. It offers flexibility in incorporating and modifying the libraries.
- PERMISSIVE: This type of license imposes a few restrictions on the distribution and modification of the software. However, it allows users considerable freedom in using and adapting the software according to their needs.
- COPYLEFT: Under this license, the software’s code can be copied, but only under the condition that the same restrictions are carried forward. This ensures that derivative works maintain the same licensing terms.
- PROPRIETARY: Users of proprietary software are typically restricted from modifying or distributing works created with the software. The usage and modification rights are retained solely by the software’s owner or licensor.
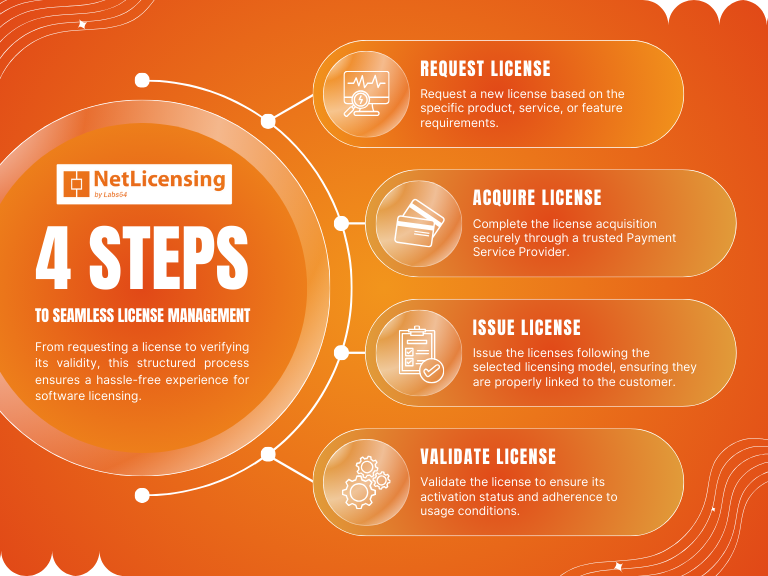
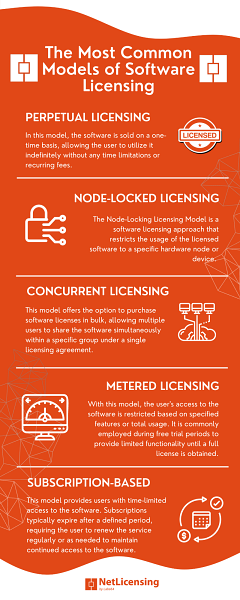
The Most Common Models of Software Licensing
- Perpetual Licensing: In this model, the software is sold on a one-time basis, allowing the user to utilize it indefinitely without any time limitations or recurring fees.
- Node-Locked Licensing: The Node-Locking Licensing Model is a software licensing approach that restricts the usage of the licensed software to a specific hardware node or device. In this model, the software is tied to the unique identification or characteristics of a particular computer or server, commonly known as the “node”.
- Concurrent Licensing: This model offers the option to purchase software licenses in bulk, allowing multiple users to share the software simultaneously within a specific group under a single licensing agreement. It simplifies software license management and ensures efficient usage across an organization.
- Metered Licensing: With this model, the user’s access to the software is restricted based on specified features or total usage. It is commonly employed during free trial periods to provide limited functionality until a full license is obtained.
- Subscription-Based: This model provides users with time-limited access to the software. Subscriptions typically expire after a defined period, requiring the user to renew the service regularly or as needed to maintain continued access to the software.
Download this infographic as PDF (229KB)
The Importance of Software Licenses
- Protection for Developers and Users: Software licenses establish clear guidelines for developers and users, outlining their rights, responsibilities, and limitations. By defining the terms of use, licenses limit liabilities and ensure both parties understand what is permissible and what is not.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Protection: Legitimate software licenses enable users to receive regular updates, patches, and security improvements from the developer. This ensures that users have access to the latest safeguards against emerging cybersecurity threats, protecting their systems and data.
- Cost Savings and Improved Efficiency: Software licenses facilitate efficient software asset management practices, helping organizations optimize their software usage and reduce operational costs. By ensuring compliance and avoiding unauthorized software usage, organizations can streamline their workflows and allocate resources more effectively.
- Mitigation of Legal Complications and Risks: Software licenses provide legal protection for both developers and users. In the event of infringement claims, licenses serve as evidence of authorized usage and help protect the developer’s intellectual property rights. Similarly, users can rely on licenses to demonstrate their compliance with legal requirements.
- Strengthened Developer-User Relationships: Software licenses provide users with essential information about their relationship to the software. By clearly defining the rights and limitations, licenses foster transparency and trust between developers and users, promoting a positive and mutually beneficial relationship.
Happy Licensing
Image Credits: Labs64